The local Dota 2 esports scene in Indonesia has been dying for the past few years. Simply put, mobile games are far more popular and successful in the country, which is why a majority of esports organizations left the PC gaming genre. Despite this, Dota 2 is still considered in many other countries to be the most superior game in the world. The International, for instance, consistently breaks the largest prize pool record in esports every single year. Furthermore, hundreds of thousands of players still actively play Dota 2, despite the game already being more than 8 years old.
Here’s the history of Dota 2 and how The International became the greatest global tournament in esports.
The History of Dota 2
It all started with Aeon of Strife, which is considered the first MOBA game. Aeon of Strife is a fan-made mod for StarCraft: Brood War. The mod became so popular that Blizzard included it in Warcraft 3. The gameplay and experience of playing Aeon of Strife are largely different from today’s MOBA game standards. However, Aeon of Strife follows the basic principles of most MOBAs. For example, the primary objective in Aeon of Strife is still to destroy the enemy base. In addition, the map also follows the three-lane layout of the MOBA map design. However, unlike most MOBAs out there, Aeon of Strife only has 4 players in each team instead of 5. There is also no PvP feature, as RedBull mentioned, so players can only fight against AIs.
If Aeon of Strife was the forerunner of the MOBA genre, Defense of the Ancients (DotA) is the game that pioneered Dota 2. Just like Aeon of Strife, DotA also originates as a mod. DotA was created as a mod for Warcraft 3 by a modder named Kyle “Eul” Sommer. The DotA mod is not very different from today’s version of Dota 2. In DotA, 10 players battle it out in 2 teams of 5 to destroy the enemy’s base. Despite the massive popularity of the DotA mod in the Warcraft community, Eul decided to leave the project behind. He also once tried to create a sequel to DotA, but this never came to fruition either. Ultimately, Eul handed the ownership of DotA to Valve.
The success of the DotA mod inspired many people to make their own version of the game. DotA: Allstars, for instance, is one of the twists that became very popular. DotA: Allstars was also created by a Warcraft modder, and his name is Steve “Guinsoo” Feak. This version of DotA is, by far, the closest resemblance to the Dota 2 game we all know today. In fact, many people even considered Allstars to be the original DotA mod since it is the version that is used in professional matches at that time.
After the success of Allstars, Guinsoo and Steve “Pendragon” Mescon — who created the DotA community center — soon joined Riot Games to assist them in developing League of Legends, and left DotA: Allstars in IceFrog’s hands. IceFrog undoubtedly has played a significant role in the entire history of DotA. Granted, he didn’t originally create Allstars or overhaul the mod, but he did create many new contents for Allstars after Guinsoo and Mescon left. Furthermore, IceFrog also ensures that the gameplay of Allstars remains balanced and that no characters are too overpowered.
At that time, DotA’s success can only happen because of the fans. The game was made by fans, for the fans, and was made big by the fans. However, things changed when League of Legends was launched in 2009 and Heroes of Newerth in 2010. The launch of these two games showed that the MOBA genre has great potential. If DotA wants to exist and compete with these two giants, it most certainly needs assistance from big gaming companies.
Fortunately, Valve came to the rescue.

In 2009, Valve announced that they will be teaming up with IceFrog. At that time, there were rumors that Valve wanted to develop a MOBA game through the partnership. However, it was only in 2010 that Valve revealed the Dota 2 project. A year later, in 2011, the beta version of Dota 2 was released and provided access to several media outlets. The beta development was a tremendous success, receiving an overall positive response from the beta testers.
Unfortunately, problems arose when Valve registered the word “DOTA” as a trademark in 2012. This decision marked the beginning of Valve’s extensive legal battle with Blizzard in the next few months. Although Blizzard did not trademark “DOTA”, they argued that the word (and its many spinoffs like DotA or Defense of the Ancients) has always been part of Blizzard and is synonymous with Warcraft. They also claimed that many of the DOTA mechanics are based on Blizzard’s Warcraft, since it is a mod of the game. Furthermore, many of the character designs in DOTA originates from Warcraft 3, according to a PC GAMER report.
Although it took several months, the legal battle between Valve and Blizzard was finally resolved. The two decided that they both have the right to use the “Defense of the Ancients” title according to their own needs. Valve will use the Dota name for its commercial products and franchises, including the Dota 2 game. On the other hand, according to Gamasutra, Blizzard will use the Dota name as a reference for its player-created content. After the fiasco, the Dota 2 development process continued smoothly.
The Birth of The International
Valve held the first The International in 2011 in conjunction with Gamescom. Interestingly, at the time, Dota 2 was technically still in beta and was not officially launched yet. So, why did Valve hold The International? Marketing. Valve provided a total prize pool of US$1.6 million, making TI the biggest prize esports tournament of its time. No other esports tournament in history was able to put up a prize pool of this caliber, and thus many people was incredibly hyped for TI. Through this buzz, Valve hopes to introduce Dota 2 to a much wider community.
Eight teams around the world and from different regions were directly invited to take part in the first-ever TI. The tournament could be spectated live in Gamescom, held in Cologne, Germany. Valve also broadcasts TI matches online so that all fans in the world can watch. Fortunately for Valve, TI was a massive hit. They were able to market the game effectively, and soon thousands of gamers flock in to try out the Dota 2.
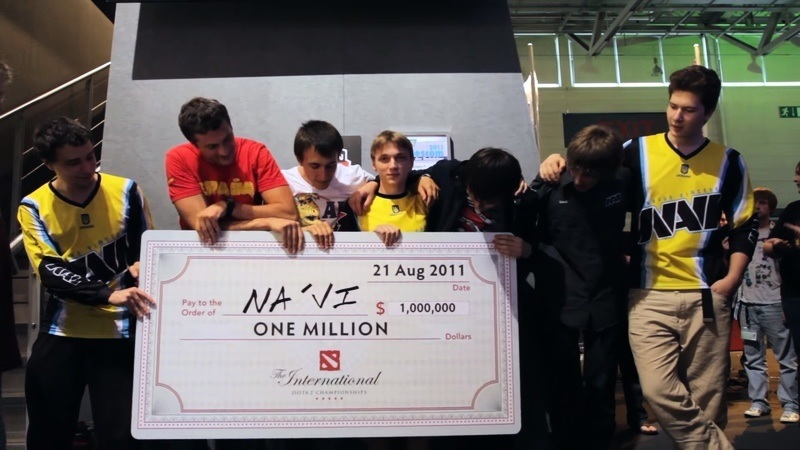

In the next few months after TI 1, Valve also continues to distribute the beta version of Dota 2. And as the player count of the game increases, the esports scene also begins to take shape. Just like the original DotA, the Dota 2 esports were initially grown by the enthusiasm and loyalty of the fans. Therefore, most Dota 2 tournaments in the olden days (excluding TI) were relatively small-scale, having prize pools of only around $25,000 USD. Even so, this was the grassroots that became the foundation of the enormous Dota 2 esports ecosystem that we know today.
In 2012, Valve held The International for the second time. The prize pool of TI2 was the exact same as TI1, which was $1.6 million USD. However, TI was now held independently by Valve in Seattle, United States. The beta version of Dota 2 was also already open to the public during this time, which means that there are far more Dota 2 followers and enthusiasts expecting TI. Furthermore, the game has also undergone several updates, significantly increasing the hero pool.
In July 2013, Valve officially launched Dota 2 on Steam, and the player count immediately skyrocketed. In June 2013, the average number of Dota 2 players only reached 210 thousand people. This figure rose to 237,000 in July and to 330.7 thousand in August. TI3 was also the start of the implementation of Valve’s crowdfunding system using the Battle Pass, and it was a major success. The International 3 prize pool was able to reach a record high of $2.8 million USD, $1.2 million more than the previous two TIs.
Since the colossal success of TI3, Valve continued to use take advantage of Battle Passes in increasing the TI prize pool. As a result, the TI prize pool has never declined even once. Last year, an Arab prince outstandingly spent over IDR 588 million in the TI10 Battle Pass. Thanks to him and hundreds of thousands of Dota 2 players, The International 10 prize pool was, yet again, able to break records and reach the $40 million USD milestone.
The growth of TI prize pools from year to year is quite massive, to say the least. For instance, The International 4 has a prize pool of around $10 million USD. 2 years later, TI6 doubled this figure and crossed the $20 million USD mark. The International 9 became the first TI with a total prize pool of more than $30 million USD.
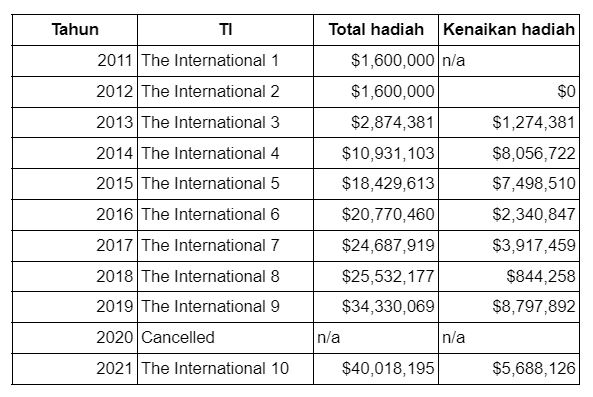
As you can see in the table above, there has been a huge spike in The International’s prize pool several times. The biggest jump occurred at The International 9, with an increase of $8.8 million USD. The difference between the TI4 and TI5 prize pool is also fairly significant. The consistent rise of The International prize goes to show how the Dota 2 community still wants to support the professional esports scene of the game. However, The International’s huge prize pool also poses its own problems.
Let’s now move to discuss the top teams that have won this prestigious tournament. Out of the 9 TIs that have been held, only one team was able to win it twice. That team is OG, which managed to win TI8 and TI9. Remarkably, they also won both consecutive TIs with the exact same composition of players.
Here’s the OG roster that won TI8 and TI9:
Anathan “ana” Pham
Topias “Topson” Taavitsainen
Sebastien “Ceb” Debs
Jesse “JerAx” Vainikka
Johan “N0tail” Sundstein – captain
And here is a list of teams that have won The International:
2011 – Natus Vincere
2012 – Invictus Gaming
2013 – Alliance
2014 – Newbee
2015 – Evil Geniuses
2016 – Wings Gaming
2017 – Team Liquid
2018 – OG
2019 – OG
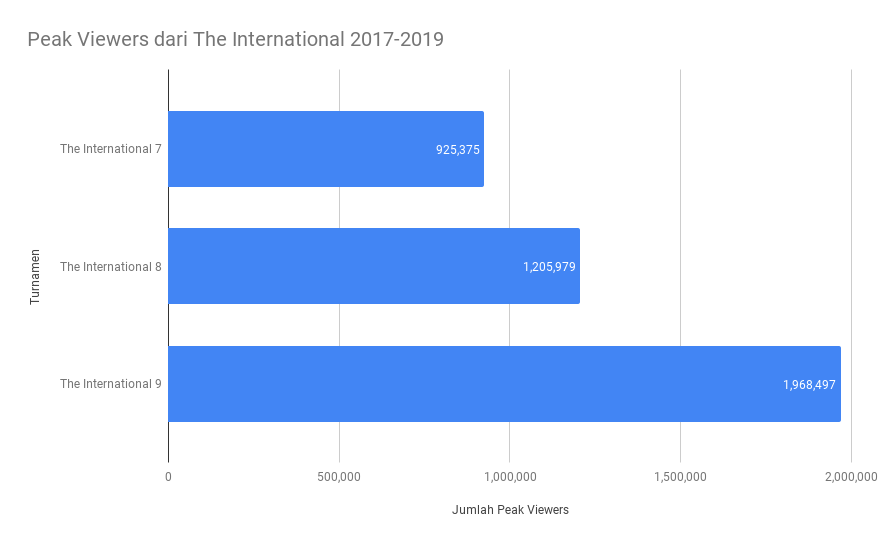
Prize pools are not the only way to measure the success of a particular tournament. Two other important factors, namely viewership numbers and watch time, can also be considered. According to data from Esports Charts, both the average number of viewers and watch hours of The International experiences an upward trend in the last four years. At TI7, the average viewer count only reached 418 thousand. This figure rose to 537.7 thousand in TI8 and to 738.9 thousand in TI9. In terms of watch time, TI7 only manages to obtain 44.3 million watch hours. In TI8, the total hours watched reached 63.9 million hours, and in TI9, that number rose to 88.4 million hours.
Unfortunately, these upward trends cannot be applied to the number of active Dota 2 players. Let’s try to observe the graph from Steam Charts of Dota 2’s player count since its launch in 2013.
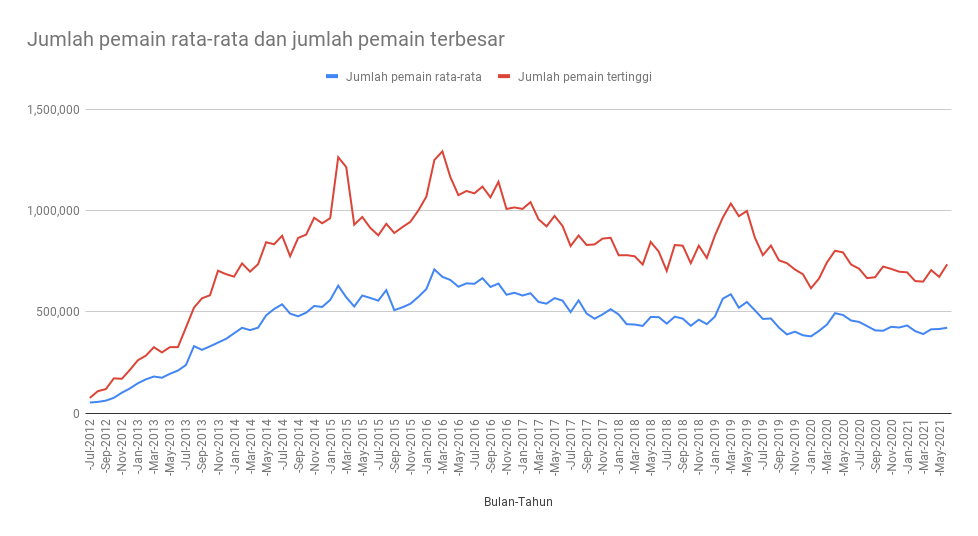
From July 2012 to July 2014, there is a general rise in the monthly player count of Dota 2. In September 2014, the player count plummeted before increasing again to 629 thousand in February 2015. Throughout its history, Dota 2’s record for the highest average number of active players was 709 thousand, which occurred in February 2016. Around the same time, Dota 2 also recorded its peak number of players, which was 1.29 million.
Since then, the average player count of the game experience a general decline, eventually reaching its lowest point in April 2018, where only 430 thousand people are playing Dota 2. However, in 2019, Dota 2 seems to have had a minor resurgence in its player base. In January of that year, the average player count was 476,000. Around 6 months later, this figure continued to rise, reaching a high of 500 thousand players. Unfortunately, the upward trend did not last, and another drought occurred in Dota 2’s player count.
At this point, many people thought that Dota 2 was officially dying and that the game’s player base will never be able to grow again. Then, the COVID-19 pandemic hit and became one of the reasons why Dota 2 experienced yet another surge in its player count. An in April of 2020, the average player number of Dota 2 hit its peak of 500 thousand players.
The Dota 2 esports scene in Indonesia
“The Dota 2 community in Indonesia today is vastly different when compared to 2014-2017,” said Yudi Anggi, a Dota 2 shoutcaster known as “Justincase”. However, this doesn’t mean that the state today’s community is worse than before. “The difference is, in the past, there were many local Dota 2 tournaments. Today, however, almost no local tournaments exist in Indonesia.,” he said when contacted by Hybrid.co.id via text message.
“But unlike the olden days, content creation in the local Dota 2 community has never been this thriving. Therefore, you can’t really say that the current state of Dota 2 in Indonesia is dead; it is simply in a different era,” said Yudi. Indeed, there are many professional players today who are actively broadcasting, such as Rusman, inYourDream. “Many fans in Indonesia today are spoiled for choice when it comes viewing live Dota 2 content,” he said. “Through these streams, we can only hope that the local Dota 2 community will continue to grow and perhaps one day experience a renaissance.”

Yudi explained that Saweria is one of the reasons why many people became interested and dived into the world of content creation. Saweria provides a simple and trusted system that allows viewers to donate to their favorite streamers. “Fans who watch the stream can be very generous in providing support to their favorite streamers,” said Yudi. “As a result, streamers become motivated to create content and entertain their viewers. In the end, this is an overall win for the entire Dota 2 community.
In a Hybrid.co.id interview with the Co-founder of Saweria, Natalia, she said that the 10 biggest receivers of support funds in Saweria are all gaming content creators. Through Saweria, some people can even generate up to IDR 44 million every month through donations alone.
On the flip side, Gary Ongko Putera, founder and CEO of BOOM Esports, has a different perspective from Yudi regarding the Dota 2 community in the country. Gary believes that the Dota 2 community in Indonesia can be quite toxic or misbehaved, which is why he is often reluctant to pay attention to them. For instance, people in the local spectrum love to support the enemy team, despite having a national team competing in the same esports tournament. “People here can be often lazy when it comes to supporting teams or players from our own country,” Gary said.
Even so, Gary still has some hope in the survival of the local Dota 2 esports ecosystem. “Luckily, Indonesia still has AG (Army Geniuses-red). As long as some organizations continue to invest in Dota 2, the local esports system will not die out,” said Gary. “I really do believe that many Indonesian Dota 2 players are incredibly talented. However, they still need proper coaching and facilities to unlock their potential and be able to fully live off of Dota 2.” Dota 2 can really be a legitimate and viable pro career option if these standards are met.
Regarding the future of the esports ecosystem, Yudi’s opinions are inlined with Gary’s. He also feels that there is still hope in the local Dota 2 esports ecosystem. However, if someone wants to become a pro Dota 2 player, he/she must be ready to face all the challenges that exist. “Because there are no local tournaments, players who want to become professionals must take their talents directly to the international arena,” said Yudi. “If they manage to find some success in SEA regional tournaments, many opportunities will eventually open up. There are still countless organizations abroad that are scouting for talents across the world. And if you skilled and lucky enough, they might just pick you up.”
Consequently, Yudi highly suggests that having decent English communication skills is imperative when it comes to getting hired by international esports organizations. “There are simply far more jobs in Dota 2 abroad, and being able to speak English can be the dealbreaker that determines if you will get or lose the job.”

According to Gary, many esports organizations have a hard time scouting new talents due to the lack of local tournaments. “Scouting new players is incredibly difficult today,” said Gary. “But fortunately, we did well for ourselves. We can often attract talents outside of Indonesia. The reputation of our esports ecosystem is actually not that bad globally, thanks to the achievements of our Dota 2 and Counter-Strike: Global Offensive teams.”
Garry also added that Indonesian esports organization provides one of the largest basic salaries when compared to other countries in the SEA region. This might be the selling point for gamers who are looking to get a career in professional Dota 2. “You can definitely earn a lot if you can become a top player. To be honest, all the best players in all games have large incomes. Unfortunately, in Dota 2, the skill ceiling is incredibly high when compared to other MOBA games. Reaching the pinnacle of the Dota 2 skill level will undoubtedly take a significant amount of work, time, and experience.
Previously, the Editor-in-Chief of Hybrid.co.id, Yabes Elia, once discussed how passion is no longer enough when pursuing a career in the world of esports. However, it is undeniable that passion maintains the longevity of the people who invest in esports. Gary and Yudi are some examples of these kinds of people. Both of them decided to stay in the Dota 2 esports ecosystem because they love and are truly passionate about the game. From a business standpoint, they could have easily migrated into the much more thriving mobile esports ecosystem. However, as Gary put it, running an esports organization would be difficult if we only focus on the business aspect.
“For me, the principle is not that complicated. Without Dota 2/CS:GO, BOOM wouldn’t have existed in the first place,” said Gary, explaining the reason why he kept the Dota 2 team. “I am truly passionate about Dota 2 and CS:GO. And it would be difficult to run a purely business-focused BOOM without my passion in mind.” He admitted that he really likes complex games. And according to him, Dota 2 is one of the most difficult games in the entire world. “No offense to other video games, but Dota 2 is far more superior in terms of complexity and depth. There are stacking mechanics, pulling creeps, proper itemizations, and tons of other minute details to learn. For the old guys like me who are more accustomed to watching complex games, I was never excited to play the simpler games of the modern era.”
Although Gary is passionate about Dota 2, he also takes into account the business side when considering his decisions. When asked whether the Dota 2 team was profitable for BOOM, Gary answered, “From a business perspective, of course, it is profitable because we frequently get to play on the international stage. However, admittedly, our profit is not that crazy large.”
On the other hand, Yudi revealed that his reason for staying loyal to shoutcasting Dota 2 was due to a matter of preference. “Honestly, I don’t really like mobile games. And I wouldn’t be able to give it my all if I was shoutcasting a game I didn’t like,” he said. “I really have to understand and be passionate about the game to give my best performance during a broadcast. If I like the game, I will be enthusiastic to study and dig up information about the game and its esports scene, which are the primary subject of discussion when I do my shoutcasting.”
In the end, as Yudi concluded, it shouldn’t really matter if someone decides to stay in Dota 2 or shift to the more popular mobile esports scene. “It goes back to each person. If someone wants to find a larger income, then go ahead and migrate to mobile esports. It is their right to choose, after all,” he said. “For me, personally, my Dota 2 career is enough to support myself financially. Although my life is not glamorous by any standards, I feel incredibly fortunate to work in the field I truly love.”
Conclusion
Eight years since its launch, Dota 2 is still played by hundreds of thousands of people around the world, which proves Valve’s effort in popularizing the game. Developing the esports ecosystem is one of Valve’s go-to methods when it comes to marketing Dota 2. Even though The International’s audience is still much lower than that of the League of Legends World Championship, TI’s huge prize pool never fails to attract public and media attention.
In Indonesia, the current state of the Dota 2 esports ecosystem has drastically changed from the old era. The bad news with the change is that local tournaments are almost non-existent. Fortunately, the good news is that there are still quite a few local esports organizations that invest in Dota 2. For this reason, Indonesians who aspire to become pros still have a chance to realize their dreams. However, they must be fully ready to compete, at the very least, in the regional stage.
Featured Image: Imgur. Translated by: Ananto Joyoadikusumo













