In the last three years, the Indonesian banking industry has been stirred with the rise of digital banks, both in the form of new banks and conversions from existing banks. As a first step, the Government released a new regulation that is expected to accommodate the needs of digital bank players through the Financial Services Authority (OJK).
POJK Number 12/POJK.03/2021 contains various provisions related to the establishment of banks and capital. Among those are the provisions for the establishment of two types of digital banks. First, the establishment of a new bank as a digital bank and second, the transformation of existing commercial banks into digital banks
In addition, the new rules are also to provide clear boundaries regarding the digital banking business considering that this trend is still relatively new in the Indonesian banking industry.
In its efforts, digital banks continue to provide literacy, therefore, people understand the business and services they run. It is while taking advantage of digital finance rapid acceleration during the Covid-19 pandemic. Based on the FICO survey in 2020, 54% of Indonesian consumers prefer to use digital channels to interact with banks, 3% mobile banking, 7% internet banking, and 14% through telephone banking.
However, we cannot forget the large groups of Indonesian people who are more comfortable with financial transactions by visiting ATMs or branch offices.
PT Bank Jago Tbk (IDX: ARTO) held a journalistic training to provide an in-depth understanding of digital banking. DailySocial had the opportunity to participate in the training held in Bali.
Several prominent observers participated, including the Research Director of the Center of Reform on Economics (CORE) Indonesia Piter Abdullah, the Indonesia Stock Exchange Business Development Advisor Poltak Hotradero, and the Director of the Center of Economic and Law Studies (CELIOS) Bima Yudhistira.
Digital bank perception
Many Indonesian people recognize digital banks as digital banking services. Also, considering it is still a brand-new business model, the understanding of digital banking is still considered blurry among the public.
Research Director of the Center of Reform on Economics (CORE) Indonesia Piter Abdullah mentions a definition to significantly distinguish digital and conventional banks. He said, a digital bank is defined as a bank along with its services where we no longer need to think about where the head office, branch offices, the number of ATMs, including the number of employee.
Similar to the GoPay and OVO digital wallet platforms, we have no idea where the money stored. With a decade of internet and smartphone adoption phenomenon, he considered the banking business would remain the same, but the delivery is started shifting.
In his opinion, this perception is reasonable considering that people are used to transacting at banks. Bank is identified as financial institution with branch offices and head office. Unlike the pre-digital era, banking competition is clear from the bank efforts to build an ecosystem. In the context of conventional banks, its ecosystem is branch offices and ATMs.
To date, the use of ATM started to be irrelevant. People are getting used to making financial transactions through mobile banking platforms and digital wallets. The banking industry has experienced massive adoption during the pandemic.
Based on OJK data, a total of 2,593 branch office networks were closed from 2017 to August 2021. These branch offices are closed in line with the bank’s digital transformation as seen from the increasing volume of digital transactions.
Piter said, whether conventional banks have not transformed into digital banks today, it does not mean they have failed to digitize. It’s more of a competition failure. It should be noted, the banking advantage factor has changed, things excelled in the past, could be a burden in the era of the digital ecosystem.
“This is not a sprint, but a marathon, determined by resilience. Moreover, digital banking is still a brand-new trend in Indonesia. Therefore, this is the reason for established banks to be prepared, not directly face-to-face but through proxies or subsidiary,” said Piter.
The above explanation is a reminiscent of Bank Jago’s Founder Jerry Ng hypothesis when he decided to acquire Artos Bank and change its name. Jerry considered Bank Artos have quite small legacies (branch offices, ATMs, and HR). In this case, his team can develop technology from scratch instead of taking a bank with thousands of branch offices.
Digital bank study case
Moreover, the Indonesia Stock Exchange Business Development Advisor, Poltak Hotradero highlighted the digital ecosystem as one of the key factors in digital banks. He took several examples of successful digital banks in the world that apply a similar model, for example KakaoBank from South Korea.
KakaoBank was founded in 2016 and is owned by internet giant Kakao Corp. In its early days, KakaoBank recorded extraordinary achievements. Within five days, KakaoBank reached 1 million users.
KakaoBank also recorded financial performance above the industry average. For example, deposit growth was at 13.65% from the industry average at 11.98%. Also, KakaoBank’s NPL was at 0.26% where the industry reached 1.78%. Meanwhile, income fee reached 30.16% of the industry’s 28.02%.
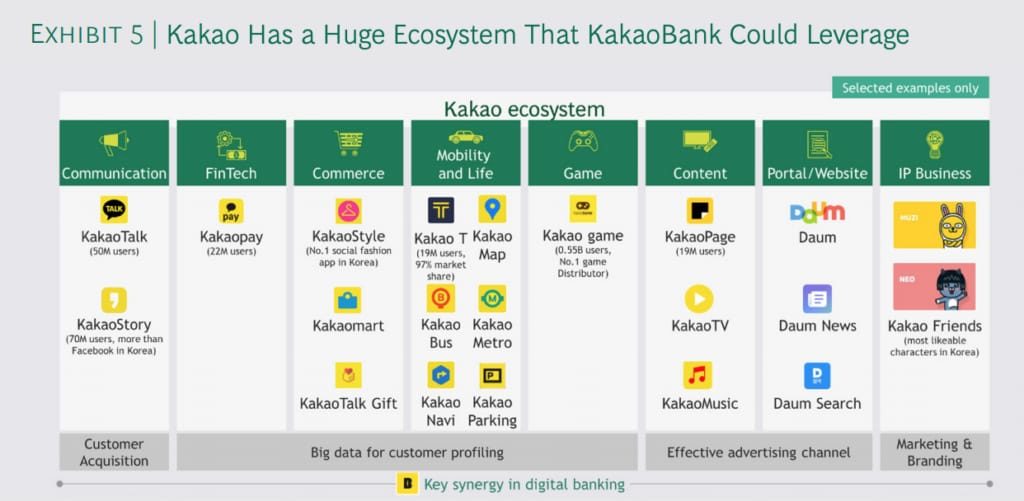
For Poltak, KakaoBank’s success also influenced by the large digital ecosystem owned by its parent company. Kakao has a diverse service portfolios, such as chat services, fintech, e-commerce, and games.
“The internet evolution has brought changes in people and money. Machines are integrated with each other thanks to the internet. This is the foundation for the development of digital banks where payments, liquidity, and analytics will be in the cloud. In other words, technology enables banks [digital] to be able to scale up faster,” he said.
In the future, Poltak mentioned the competition of three types of banks, conventional banks, digital banks, and embedded banks. He defines embedded bank (Bank-as-a-Service/BaaS) as a service that has been operating digitally since day one and has entered the (native) ecosystem. He also said that embedded banks would become part of the plumbing system for corporate or individual financial services.
“Digital platforms will facilitate synergies with other digital financial services, such as investment and insurance services. However, it is important to note that the biggest cost and risk of the digital transition is failure to maintain market share and segments. These factors can turn banks irrelevant,” he added.
Therefore, he highlighted that digitalization is a competitive necessity. We should not let the financial sector only delegate its role through banks, given the huge business potential and services. He believes market expansion is important for developing digital banks considering a large number of unexplored market segments in Indonesia and can only be served through digital.
Digital bank projection
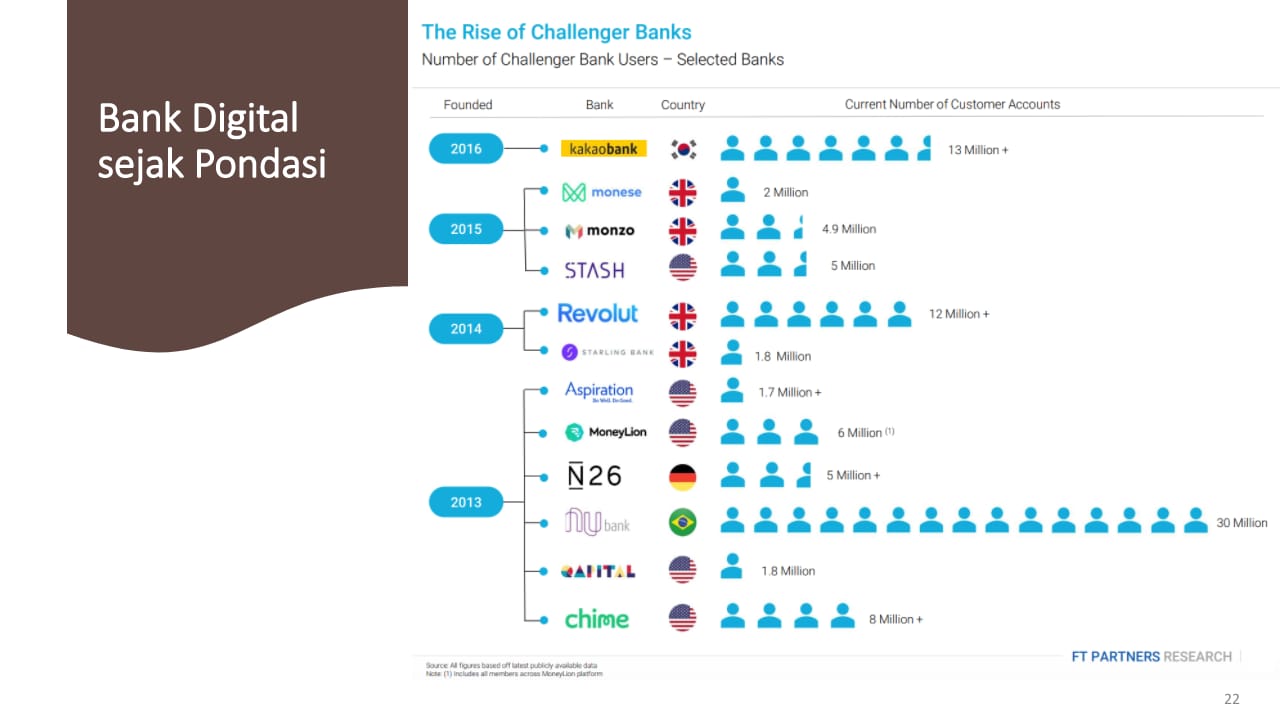
According to his study, Director Center of Economic and Law Studies (CELIOS) Bhima Yudhistira divides digital banks into three models, direct banks, neobanks, and challenger banks.
He explained that direct banks enlarge opportunities for banking services, such as savings and digital loan channeling. Furthermore, neobank operates as a fully digital bank, without branch offices, but with a mobile application. Meanwhile, challenger banks are said to be revolutionizing the way transactions, new loan models, and personal finance.
Bhima said the global potential accumulation of challenger bank and neobank markets could reach $578 billion in 2027, according to a Medici Research report.
We try to take other sources to provide a thorough definition, especially on neobanks and challenger banks. Citing from FinTech Magazine, neobank offers flexibility to various services, including payroll and expense management. In addition, neobank also offers corporate financial solutions to address the challenges of MSMEs.
The API presence helps to integrate business flows with banking requirements. However, neobanks do not have a banking license as they operate by relying on partner banks. Therefore, they cannot offer traditional banking services.
Meanwhile, challenger banks use technology to streamline the banking process. However, challenger banks also maintain a physical presence to operate fintech services. The challenger banks scope is generally much smaller than the mainstream banking sector. It is estimated that there are currently 100 challenger banks globally.

Unlike neobank, challenger bank has a bank license and can offer customers a wide range of traditional and digital banking services. These traditional banking services can be accessed and utilized more accommodatively than commercial banks.
Furthermore, Bhima considered that digital banks offer a number of advantages, both for individuals and business players. At the individual level, digital banks increase customer literacy in other financial products, such as investments. According to World Bank data in 2020, the share of stock market capitalization to GDP is still relatively small. The emergence of digital banks is projected to encourage investment interest.
In addition, digital banks can encourage financial control efforts in the MSME sector with financial transparency and efficiency. Moreover, business players can get access to financing channeled by digital banks through channeling schemes.
“To date, banks do not compete with technology, but with high interest rates. Moreover, digital bank suddenly appeared, offering easy services and access to capital. Currently, Indonesia has 65 million MSMEs and some of them are yet to receive loans. Digital banks can add to that financing capacity. If Indonesia wants to restore the economy to the level of 5%, its credit growth must triple,” he explained.
Based on data-driven credit scoring, digital banks can continue to grow by extending credit to unbankable segments. In the future, this loan disbursement can use the customer transaction rating indicator on e-commerce, food delivery, or ride-hailing platforms.
–
Original article is in Indonesian, translated by Kristin Siagian













